Investing in Jordan

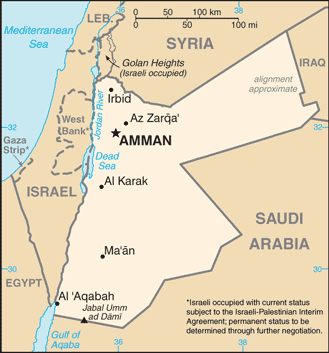
Jordan's economy is among the smallest in the Middle East, with insufficient supplies of water, oil, and other natural resources, underlying the government's heavy reliance on foreign assistance. Other economic challenges for the government include chronic high rates of poverty, unemployment, inflation, and a large budget deficit. Since assuming the throne in 1999, King ABDALLAH has implemented significant economic reforms, such as opening the trade regime, privatizing state-owned companies, and eliminating most fuel subsidies, which in the past few years have spurred economic growth by attracting foreign investment and creating some jobs. The global economic slowdown, however, has depressed Jordan's GDP growth. Export-oriented sectors such as manufacturing, mining, and the transport of re-exports have been hit the hardest. The Government approved two supplementary budgets in 2010, but sweeping tax cuts planned for 2010 did not materialize because of Amman's need for additional revenue to cover excess spending. The budget deficit is likely to remain high, at 5-6% of GDP, and Amman likely will continue to depend heavily on foreign assistance to finance the deficit in 2011. Jordan's financial sector has been relatively isolated from the international financial crisis because of its limited exposure to overseas capital markets. Jordan is currently exploring nuclear power generation to forestall energy shortfalls.
Central Bank of Jordan - http://www.cbj.gov.jo/
Jordan Dubai Capital - http://www.jd-capital.com/
The Arab Jordan Investment Bank - http://www.ajib.com/
The Cairo Amman Bank - http://www.ca-bank.com/
The Jordan National Bank - http://www.ahli.com/
The Jordan Kuwait Bank - http://www.jordan-kuwait-bank.com/
Travertine Company - http://www.travco.com.jo/
Countries that border Jordan: Israel | Syria | Iraq | Saudi Arabia
Learn more:
Back to Country Investing



