Investing in North Korea
North Korea, one of the world's most centrally directed and least open economies, faces chronic economic problems. Industrial capital stock is nearly beyond repair as a result of years of underinvestment, shortages of spare parts, and poor maintenance. Large-scale military spending draws off resources needed for investment and civilian consumption. Industrial and power output have stagnated for years at a fraction of pre-1990 levels. Frequent weather-related crop failures aggravated chronic food shortages caused by on-going systemic problems, including a lack of arable land, collective farming practices, poor soil quality, insufficient fertilization, and persistent shortages of tractors and fuel. Large-scale international food aid deliveries have allowed the people of North Korea to escape widespread starvation since famine threatened in 1995, but the population continues to suffer from prolonged malnutrition and poor living conditions. Since 2002, the government has allowed private "farmers' markets" to begin selling a wider range of goods. It also permitted some private farming - on an experimental basis - in an effort to boost agricultural output. In October 2005, the government tried to reverse some of these policies by forbidding private sales of grains and reinstituting a centralized food rationing system. By December 2005, the government terminated most international humanitarian assistance operations in North Korea (calling instead for developmental assistance only) and restricted the activities of remaining international and non-governmental aid organizations. In mid-2008, North Korea began receiving food aid under a US program to deliver 500,000 metric tons of food via the World Food Program and US nongovernmental organizations; but Pyongyang stopped accepting the aid in March 2009. In December 2009, North Korea carried out a redenomination of its currency, capping the amount of North Korean won that could be exchanged for the new notes, and limiting the exchange to a one-week window. A concurrent crackdown on markets and foreign currency use yielded severe shortages and inflation, forcing Pyongyang to ease the restrictions by February 2010. In response to the sinking of the South Korean destroyer Cheonan and the shelling of Yeonpyong Island, South Korea's government cut off most aid, trade, and bilateral cooperation activities, with the exception of operations at the Kaesong Industrial Complex. The year 2012 will be the 100th anniversary of Kim Il-sung's birthday. The North Korean government often highlights its 2012 goal of becoming a "strong and prosperous" nation. Attracting foreign investment, especially from neighboring China, will be a key factor for improving the overall standard of living. Nevertheless, firm political control remains the government's overriding concern, which likely will inhibit changes to North Korea's current economic system.
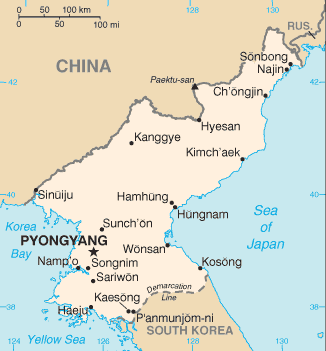
Countries that border North Korea: China | Russia | South Korea
Learn more:
Back to Country Investing



